

Both a small interfering RNA (siRNA) and an antibody targeted to ASGR1 were found to lower cholesterol in mice through a similar mechanism. 4 now show that genetic deletion of Asgr1 in mice lowers serum and cholesterol and promotes cholesterol excretion through a mechanism involving stabilization of liver X receptor (LXR), without activation of sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP1) and lipogenesis. Interspecies Information Highest antigen sequence identity to the following orthologs: Mouse ENSMUSG00000020884 (76) Rat. Antibody validation: Validated for Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry and Western Blot. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody was used to detect the primary antibody.
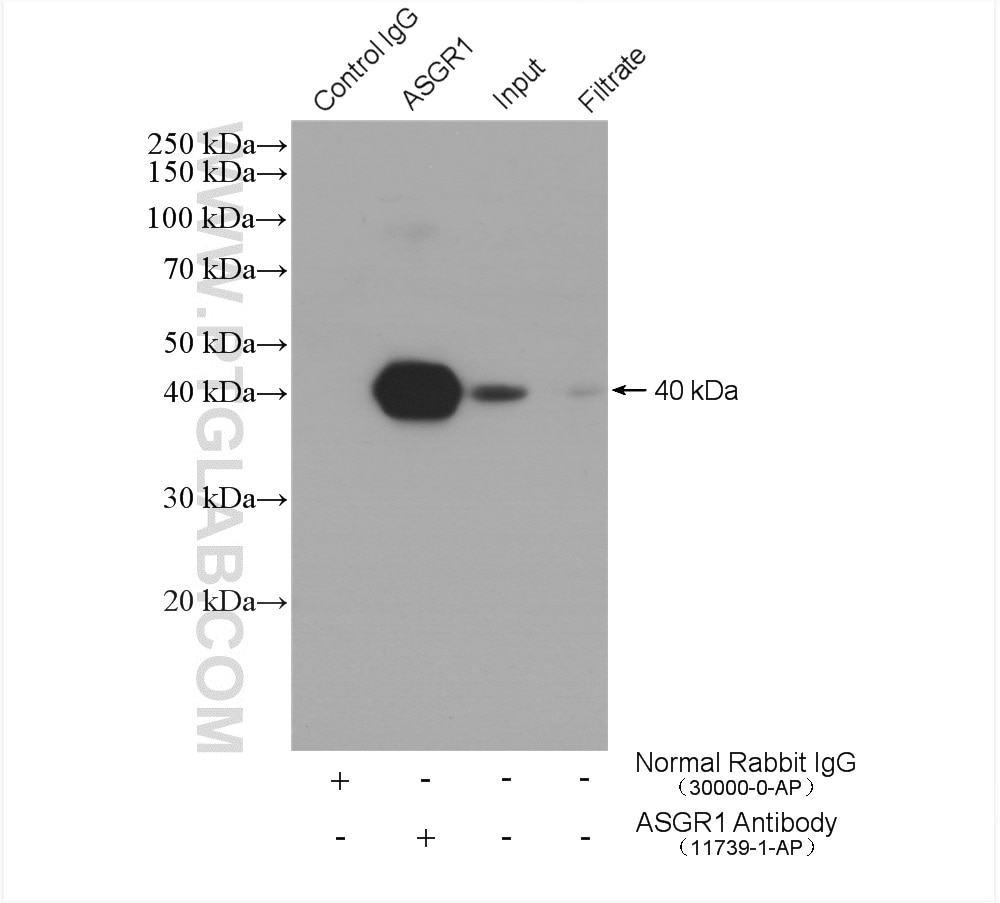
Proteins were transferred to a membrane and probed with a ASGR1 Polyclonal Antibody (Product PA5-32030) at a dilution of 1:3000. The asialoglycoprotein receptor may facilitate hepatic infection by multiple viruses including hepatitis B, and is also a target for liver-specific drug delivery.
Genetic variants that reduce function of the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR) found within the gene encoding its primary component ( ASGR1) have been reported to be associated with reduced levels of cholesterol and protection from coronary artery disease 3. New research reports that targeting the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR1) in mice promotes cholesterol excretion through a mechanism involving stabilization of LXR without lipogenesis activation. Rabbit Polyclonal Anti-ASGR1 Antibody against Human asialoglycoprotein receptor 1. Western blot analysis of ASGR1 was performed by separating 50 µg of mouse tissue extract by 10 SDS-PAGE. Manufacturer: Proteintech Group Inc 117391AP150UL. Our understanding of cholesterol metabolism has been substantially enhanced by discoveries in human genetics, which have led to several new therapeutic approaches to reducing blood cholesterol and risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1, 2. ASGR1 Rabbit anti-Human, Mouse, Rat, Polyclonal, Proteintech.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
